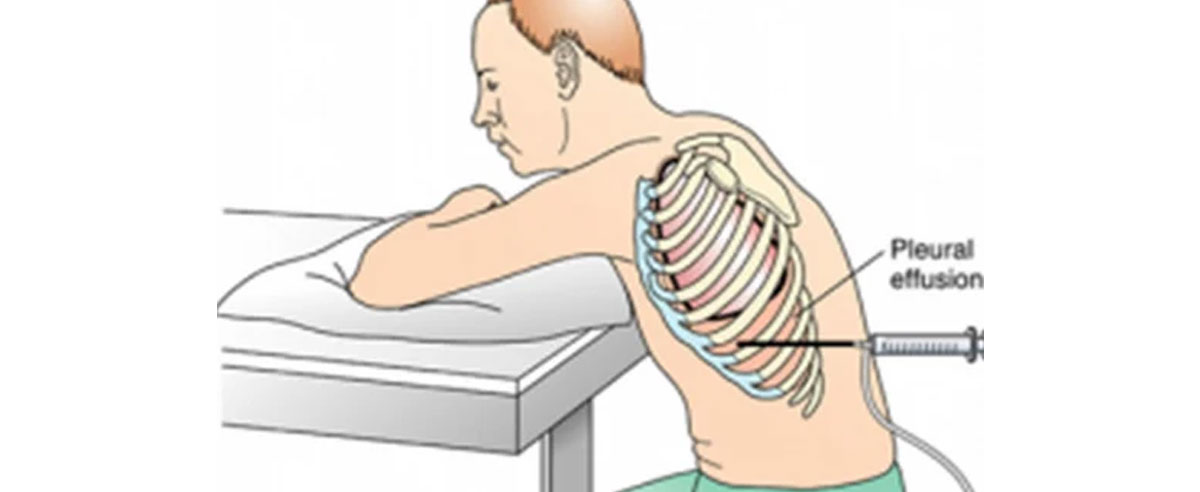
Pleural Tapping
Pleural tapping, also known as thoracentesis or plecentesis, is a medical procedure used to remove excess fluid or air that has accumulated in the pleural space, the space between the membranes surrounding the lungs (the pleura). Here's a brief overview of pleural tapping:
Procedure:
- Local Anesthesia: The patient is usually given a local anesthetic to numb the skin and underlying tissues at the site where the procedure will be performed.
- Needle Insertion: A thin, hollow needle or catheter is inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space under the guidance of ultrasound or fluoroscopy.
- Fluid or Air Removal: Once the needle is in place, excess fluid or air is withdrawn and collected in a sterile container.
- Monitoring: The patient's vital signs and oxygen levels are monitored during the procedure to ensure safety.
Uses:
- Diagnostic: Pleural tapping can help diagnose the underlying cause of pleural effusion by analyzing the removed fluid. It may reveal infections, cancer cells, or other abnormalities.
- Therapeutic: Removing excess fluid or air can relieve symptoms like chest pain and difficulty breathing and improve lung function.
Risks:
- Pleural tapping is generally considered safe, but there are some potential risks, including infection, bleeding, pneumothorax (especially in cases of pleural effusion removal), and injury to nearby structures.