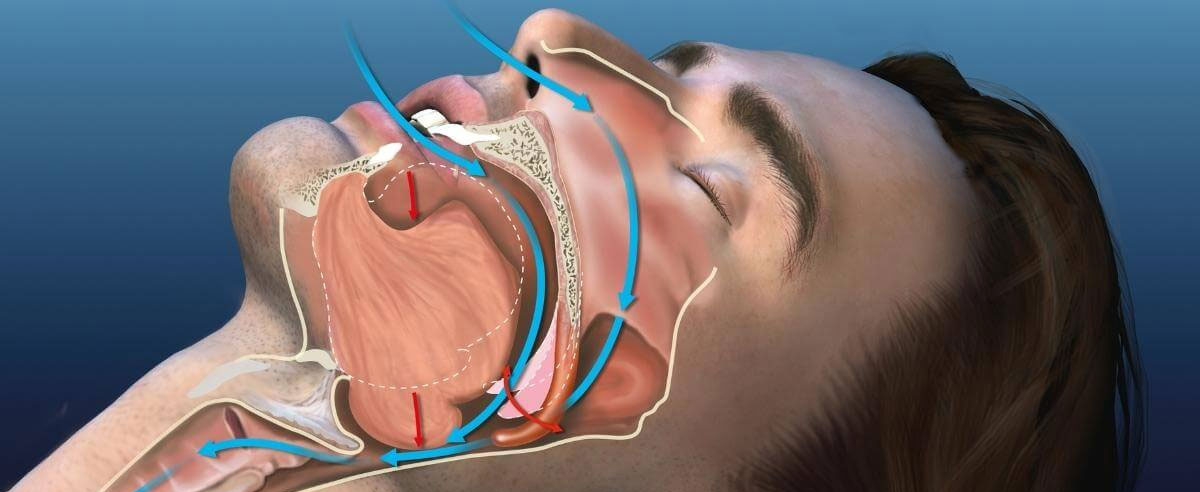
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, known as apneas, occur when the muscles in the throat relax excessively, causing a temporary blockage or obstruction of the upper airway. Here's a brief overview of OSA:
Causes
OSA typically occurs when the muscles at the back of the throat become too relaxed during sleep, leading to a partial or complete blockage of the airway. This often happens due to anatomical factors (e.g., narrow airway, large tonsils) and lifestyle factors (e.g., obesity, smoking) that contribute to airway narrowing.
Symptoms:
The most common symptoms of OSA include loud and chronic snoring, pauses in breathing or choking sounds during sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, morning headaches, and irritability. OSA can also contribute to other health problems such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is typically based on a combination of factors, including a thorough medical history, a sleep evaluation conducted in a sleep laboratory (polysomnography), and home sleep tests. These tests monitor various parameters during sleep, such as oxygen levels, heart rate, and airflow, to determine the severity of the condition.
Treatment:
Treatment for OSA aims to keep the airway open during sleep and improve oxygen flow. Common treatment options include:
© Dr. Shilpa Jain. All Rights Reserved.