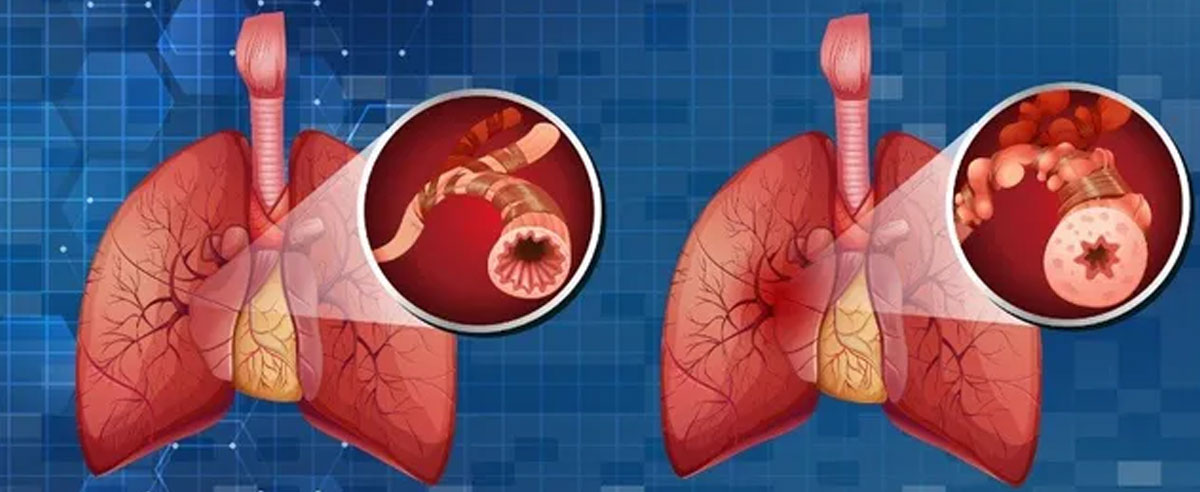
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive and chronic lung condition characterized by airflow limitation and breathing difficulties. Here's a brief overview of COPD:
Causes
The primary cause of COPD is long-term exposure to irritants and toxins, with cigarette smoking being the most common risk factor. Other factors can include occupational exposure to pollutants and genetics.
Types
COPD includes two main conditions:
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of COPD include:
Pathophysiology:
COPD is characterized by the progressive destruction of lung tissue and the inflammation of airways. This leads to reduced airflow in and out of the lungs, resulting in the hallmark symptoms.
Diagnosis
COPD is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, lung function tests (spirometry), and imaging (such as chest X-rays or CT scans).
Treatment
COPD management includes:
COPD Progression:
COPD is a progressive disease, meaning it tends to worsen over time. However, early diagnosis and management can slow down the progression and improve symptoms.
© Dr. Shilpa Jain. All Rights Reserved.